Brand Maker Industry
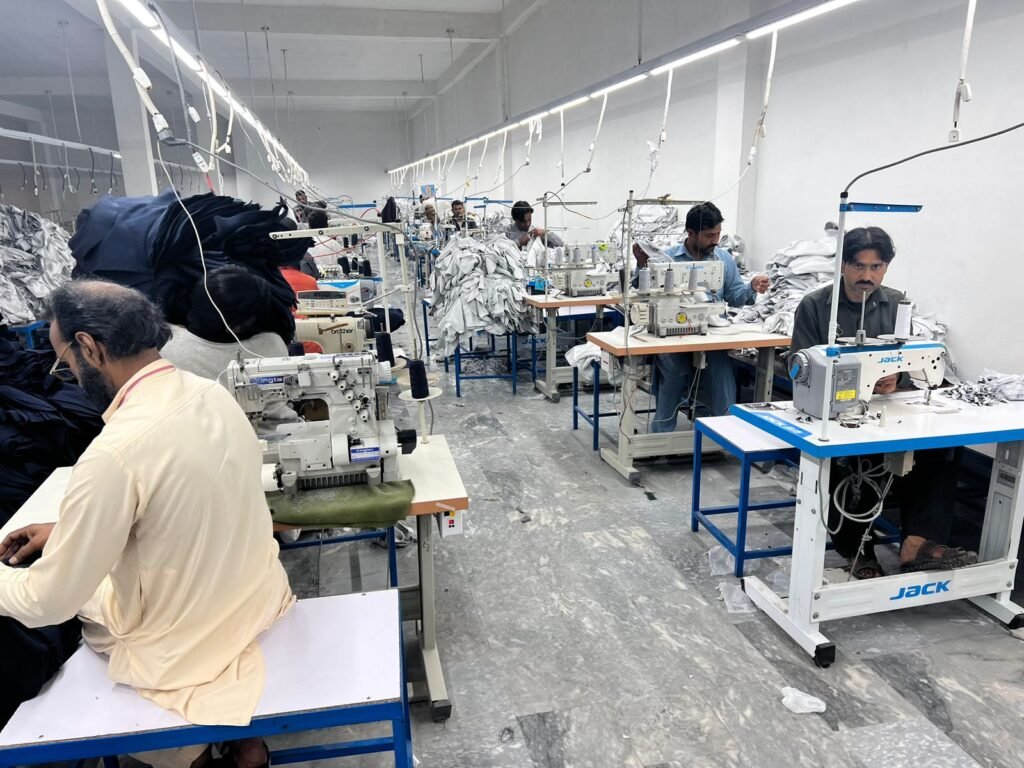
At Brand Maker Industry, we specialize in creating customized fabrics tailored to your unique vision. Whether you want innovative textures, exclusive designs, or fabric that sets you apart from other brands, we help you build a strong identity through originality.
Our expertise in private label and white label solutions allows brands to choose their own fabric weight, color, finish, and style — ensuring that every product truly reflects your brand’s personality.
👉 Your Brand. Your Fabric. Your Identity.
Knitted fabric & Process How to make the Fabric
Knitted fabric is widely used in products that need stretch, comfort, flexibility, and breathability — such as sportswear, casual wear, uniforms, underwear, safety T-shirts, and medical textiles.
Where Knitted Fabric is Used?
🔹 Apparel / Clothing:
T-Shirts & Polo Shirts
Hoodies & Sweatshirts
Joggers & Track Pants
Leggings & Yoga Pants
Sports Bras, Activewear & GymWear
Undergarments, Socks & Hosiery
Casual Dresses & Tops
🔹 Safety & Workwear:
Safety T-Shirts (high-visibility / reflective)
Polo Shirts for uniforms
Thermal Innerwear
🔹 Home Textiles:
Blankets
Jersey Bedsheets
Cushion Covers
🔹 Medical & Technical Uses:
Bandages & Compression Wear
Elastic Fabrics for supports/braces
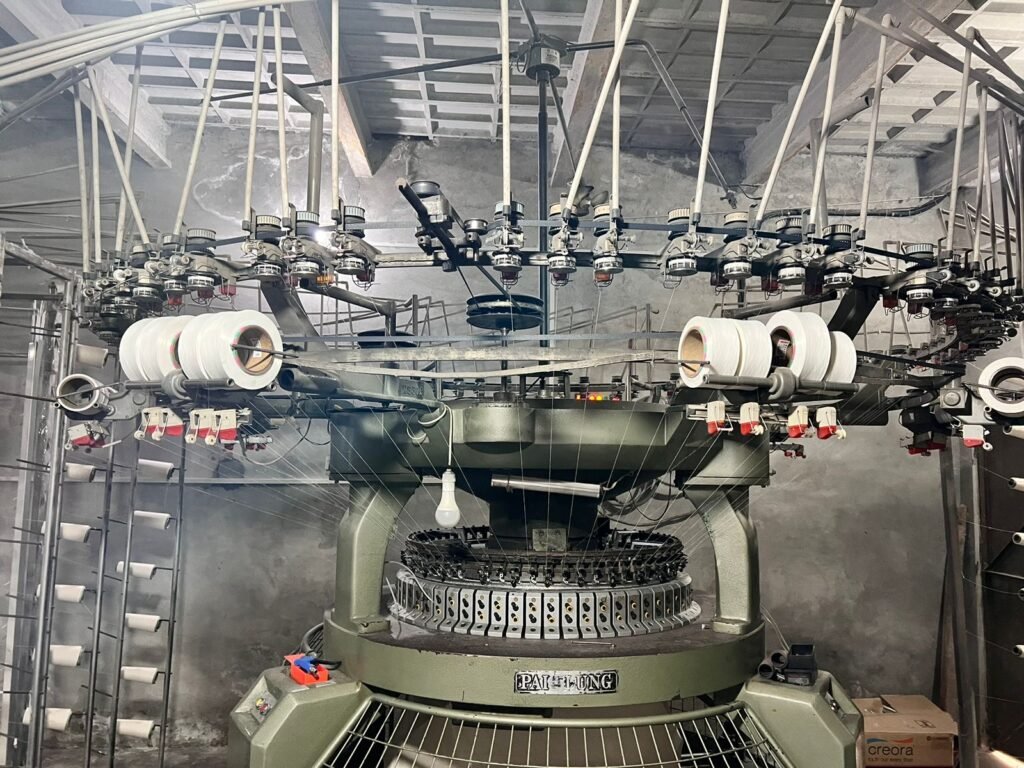
Knitted fabric Process & production process
How Fabric is Made
1. Fiber Production
First, fibers are obtained.
Natural fibers: cotton, wool, silk, flax (linen).
Synthetic fibers: polyester, nylon, acrylic.
2. Yarn Making (Spinning)
Fibers are spun together to make yarn (thread).
Example: cotton → spun into cotton yarn.
3. Fabric Formation
There are 2 main methods:
Knitting
Loops of yarn are interlocked.
Creates stretchable fabric (used in T-shirts, sportswear, socks, etc.).
Weaving
Two sets of yarns are interlaced at right angles.
Creates stronger, non-stretch fabric (used in denim, shirts, trousers, jackets).
(There are also non-woven fabrics like felt or medical disposables, made by bonding fibers directly.)
4. Dyeing & Printing
Fabric is dyed into different colors.
Printing adds patterns, logos, or designs.
5. Finishing
Special treatments to improve fabric performance.
Examples: waterproofing, fire resistance, wrinkle-free, soft finish.









